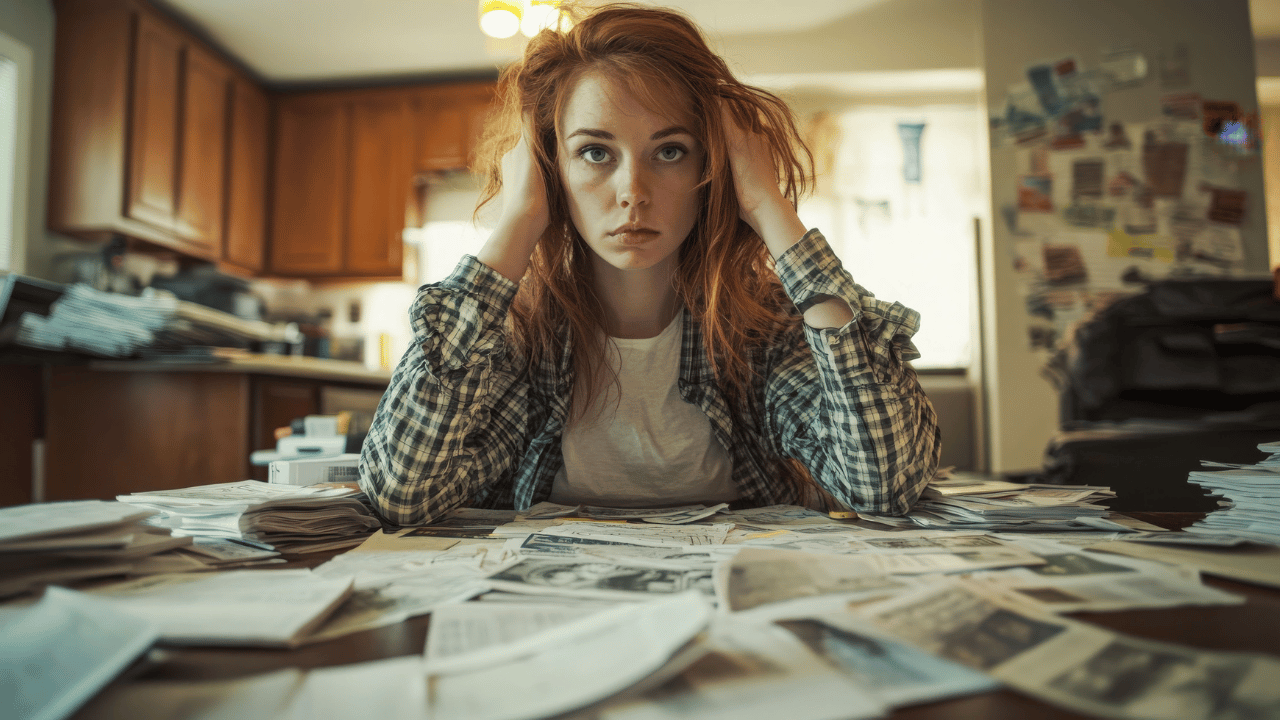
It often starts on an ordinary Tuesday. You wake up tired, even after a full night in bed. By lunchtime, your shoulders are tight, your patience is thin, and you’re already counting the hours until you can log off.
That’s how stress burnout shows up for many people in the United States. It doesn’t always arrive with a dramatic breaking point. It can creep in through small signals—shorter replies to loved ones, more scrolling at night, and a mind that won’t slow down.
When stress stops being “manageable,” the body can get stuck in high alert. Over time, that strain can lead to emotional exhaustion, sleep problems, and health changes that feel confusing at first. You may still be getting things done, but it starts to cost more than it should.
This is where therapy for burnout can make a difference. Instead of quick tips, stress management therapy offers a structured way to see the pattern, name what’s driving it, and build skills that hold up on hard weeks. Burnout recovery tends to work best when it’s steady, supported, and tied to real life—workload, relationships, and personal expectations.
If you’re thinking about therapy and parts of this feel familiar, you can call 510-877-0950 or schedule an online appointment when you’re ready: https://bewellcounselingtx.com/book-an-appointment/.
Key Takeaways
- stress burnout often builds slowly through sleep issues, irritability, and nonstop mental noise.
- emotional exhaustion can look like “functioning,” but with less joy, patience, and clarity.
- Burnout recovery usually requires more than rest; it takes repeatable tools and support.
- therapy for burnout can help identify triggers and reset how your nervous system responds.
- stress management therapy focuses on skills you practice between sessions, not just advice.
- Many people in the United States seek help once stress begins affecting health and relationships.
From “Just Busy” to Burnout: How Stress Quietly Escalates
It often starts with a packed calendar and a sense of pride. But the “busy season” can go on forever. Stress burnout can become normal, even when your body warns you.
Modern stress makes it hard to tell effort from strain. Pressure becomes the norm, affecting sleep, mood, and focus. What looks like hard work can actually be exhaustion.
What burnout is (and isn’t): emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion over time
Burnout is long-term emotional, physical, and mental depletion from constant pressure. It’s not just a bad week or feeling tired after a deadline. Burnout grows when demands never stop and recovery is always behind.
Feeling emotionally drained is a key sign, but not the only one. People may feel cynical, have a harsh inner critic, or doubt their work’s value. Tasks seem harder, and achievements feel smaller.
| What changes | Everyday stress | Burnout pattern |
| Energy level | Tired but able to rebound after rest | Ongoing depletion; fatigue lingers even after a weekend |
| Mindset toward work | Concerned, but still engaged | Detached or cynical; dread builds before the day starts |
| Performance | Short dips during crunch times | Reduced professional efficacy; more mistakes and slower recovery |
| Recovery | Relief after a break or finished project | Relief is brief; overload returns fast because the system is still strained |
Common ways burnout creeps in: waking up tired, a mind that won’t switch off, and shrinking patience in relationships
Burnout doesn’t come suddenly. It starts with small changes: waking up tired, needing more caffeine, and feeling mentally exhausted early. Sleep might not fix it, and exhaustion persists.
A mind that can’t relax is another sign. You might think about work or second-guess yourself even when trying to unwind. Emotional burnout can also lead to less patience at home or with friends.
Why modern pressure hits harder: high work expectations, constant social comparison, and digital overload
Today’s work environment values speed and constant improvement. For many, high stakes are normal. This can lead to burnout that affects identity and purpose.
Constant social comparison adds to stress. Even a quick scroll can make you feel pressured to do more. Digital overload keeps your nervous system on edge for days.
stress burnout Warning Signs That It’s More Than Everyday Stress
Some stress goes away with a weekend break. Burnout doesn’t. It keeps coming, making your body think it’s always in danger.
Chronic stress signs start to pile up. You might notice patterns that feel hard to shake, even with good habits.
Emotional burnout symptoms
Emotional burnout can start quietly. Instead of feeling sad, you might feel numb or distant from things you love.
Irritability often follows. Small things can feel overwhelming, causing you to snap without meaning to.
Other signs include mood swings and feeling unaccomplished. Even when you succeed, it might not feel like it’s enough.
Cognitive signs
Burnout warning signs can affect your thinking. You might find yourself reading the same email over or losing your train of thought.
Racing thoughts, often about work, can be constant. Making decisions can feel slow and heavy.
Physical stress signals
Stress shows up in your body. You might get headaches, stomach issues, or feel tense in your shoulders and jaw.
Sleep problems are common. Some people can’t sleep because their mind won’t calm down. Others wake up early, worried.
When sleep issues persist, you might feel tired all the time. Getting sick more often can be a sign of the same stress response.
Work and relationship red flags
Look out for a lack of motivation. You might delay tasks or do the minimum to get by.
At home, you might pull away or cancel plans. Feeling overwhelmed can make you want to isolate, which can worsen emotional burnout.
| What you can observe | How it may show up day to day | Why it matters |
| Short fuse and irritability | Snapping at loved ones, feeling “on edge” in traffic or meetings | Often signals burnout warning signs, not just a bad mood |
| Foggy focus and decision fatigue | Slow reading, second-guessing, avoiding choices | Common stress burnout symptoms when mental load stays high |
| Body tension and stress symptoms | Headaches, stomach tightness, jaw clenching, rapid heartbeat | Chronic stress signs can build even when you “look fine” |
| Ongoing sleep problems | Trouble falling asleep, waking at 3 a.m., never feeling rested | Poor sleep can keep the stress response activated longer |
| Slipping performance and pulling back | Lower motivation, missed deadlines, canceling plans | Work and relationship strain often drives people to seek help |
Many people try to fix it themselves with motivational quotes or breathing videos. But if it doesn’t work, your brain might still see everyday tasks as threats.
Case Study: How Work Stress Therapy Helped a High-Performer Reset
A high-performing professional felt “on” all the time. Despite good metrics, they felt heavy and stressed. This stress was affecting their work and home life.
They woke up tired, even after a full night’s sleep. Small problems at work felt personal. They feared they were not as good as they used to be.
Presenting concerns
The first sessions revealed their struggles. They felt low in energy and motivation. Cynicism had replaced their pride.
They could still perform, but it took more effort. The sense of impact was fading. This was a sign of high achiever burnout.
What surfaced in sessions
Perfectionism was a big part of their story. Any slip was seen as failure. This self-criticism led to longer hours and fewer breaks.
They had a habit of overextending. Saying “no” felt risky, so tasks piled up. Boundaries were unclear, and needs were rarely named.
Unprocessed emotions were present but muted. Frustration and grief were hidden. This fueled detachment and a shorter fuse, common in stress burnout.
Skills that changed the pattern
Grounding routines were introduced to interrupt spirals. These quick practices helped the body relax before the mind got caught up in worst-case scenarios.
Cognitive reframing challenged exaggerations and all-or-nothing thinking. Instead of fearing failure, they learned to balance their views.
Emotional regulation skills were practiced in small steps. They learned to name feelings without judging them. They also learned structured problem-solving.
Boundary-setting and assertiveness were seen as skills, not traits. They focused on clear requests, realistic timelines, and protecting recovery time.
Progress markers
Progress was tracked by daily function, not just mood. They felt calmer and thought clearer in the afternoon. Sleep became more consistent, with fewer middle-of-the-night wakeups.
After stressful moments, recovery was faster. They noticed the stress response earlier and chose a next step. These small resets added up in burnout recovery.
| Focus Area | Early Pattern | In-Therapy Practice | Week-to-Week Marker |
| Energy and pacing | Running on empty; skipping breaks | Workload mapping; planned pauses; time-boxing | Fewer late nights; steadier afternoon energy |
| Thought habits | Catastrophic predictions; harsh self-talk | cognitive reframing; evidence checks; balanced statements | Less rumination; quicker return to task |
| Emotional load | Numbness, irritability, detachment | emotional regulation; mindful labeling; paced breathing | More stable mood; fewer “blow-up” moments |
| Boundaries at work | Automatic yes; unclear limits | Assertive scripts; priority rules; meeting guardrails | Clearer timelines; fewer last-minute rescues |
| Recovery after stress | Stays activated for hours | Grounding routine; short decompression plan | Faster calm; improved sleep patterns |
Burnout Recovery in Therapy: What Actually Happens and Why It Works
Therapy for burnout is most effective when it’s structured and practical. It’s not just a place to vent. Stress burnout often stems from work pressure, high self-standards, and life demands that pile up over time. A therapist helps you understand these patterns and change them.
Evidence-based therapy is different from quick fixes. It targets the root causes of your stress response. This way, your body and mind can settle down. Over time, your system learns safer ways to react.
Identifying root causes: mapping triggers across work dynamics, personal expectations, and life circumstances
Early sessions often focus on mapping triggers. This includes workload spikes, unclear roles, conflict, and a culture that rewards constant availability. It also includes personal expectations like perfectionism, people-pleasing, and fear of letting others down.
Therapy also looks outside of work. Caregiving, financial strain, health issues, and family stress can keep your nervous system on edge. The goal is to spot where you are overextending and where boundaries are thin.
Rewiring the stress response: moving from fight-or-flight reactivity to a calmer, more regulated baseline
When stress burnout is chronic, your body may always think danger is near. Therapy aims to move you from fight-or-flight to a steadier baseline. You learn to notice early cues, slow the spiral, and recover faster after a hard moment.
This is built on a simple idea: the brain can change. With consistent practice, you can unlearn old stress loops and build new pathways that support sleep, focus, and steadier mood.
Evidence-based approaches that may be used: CBT, ACT, and mindfulness-based therapy
CBT for burnout focuses on thought patterns that pour fuel on pressure, like “I’m failing” or “If I rest, I’ll fall behind.” A therapist helps test those thoughts, replace them with balanced ones, and add skills like assertive communication, pacing, and relaxation drills.
ACT therapy builds psychological flexibility. You practice making room for tough feelings without getting pushed around by them, while taking steps tied to your values. This can loosen self-criticism and help you reconnect with meaning.
Mindfulness-based therapy trains attention so your mind doesn’t stay stuck in rumination. Practices like breath work, body scans, and short meditations can reduce automatic reactions and improve awareness of stress signals.
Beyond coping tips: practicing between sessions so tools become second nature
Progress usually comes from what happens between sessions. You may track triggers, practice grounding, and rehearse new responses before the next high-stakes meeting or family conflict. Repetition is what turns tools into habits.
- Brief emotion tracking to spot patterns and early warning signs
- Cognitive reframing practice to reduce all-or-nothing thinking
- Body relaxation training, like paced breathing or muscle release
- Mindfulness routines that fit real life, not perfect schedules
- Problem-solving plans that break big tasks into smaller steps
Building protection against relapse: strengthening boundaries, values alignment, and long-term resilience
Burnout recovery also includes relapse prevention. Therapy can help you set boundaries that hold, align your calendar with your values, and plan for predictable crunch times. The focus shifts from “getting through the week” to maintaining a stable pace.
A therapist can also spot blind spots, help you reset after setbacks, and keep the plan realistic. That support matters when old habits try to return during busy seasons.
Access and fit: in-person care vs. virtual therapy Texas options for privacy and flexibility
Many people choose virtual therapy Texas sessions for privacy, flexible scheduling, and less time lost to commuting. Some clients find they open up more at home, which can speed skill practice. In-person care can feel more grounding for others, when home is not a calm space.
Both formats can deliver strong evidence-based therapy when sessions are consistent. In Texas, availability can include metro areas and nearby communities, with options that reach places like Sugar Land and San Antonio through virtual or in-person care.
| What to compare | In-person therapy | Virtual therapy Texas |
| Privacy and comfort | Private office setting, fewer home distractions, clear separation from work and family life | Often feels more private for busy professionals, with easier access from home or a parked car |
| Scheduling and access | May require commute time and fixed office hours, which can be hard during peak workload weeks | More flexible for morning, evening, or weekend slots when offered by the clinic |
| Skill practice support | Good for guided breathing, grounding, and role-play with fewer interruptions | Allows real-time practice in your actual environment, like preparing for a meeting at your desk |
| Fit signals to look for | Deep listening, a collaborative plan, and practical tools that feel usable after each visit | Clear structure, good session flow, and noticeable small improvements within a few weeks |
| Personalization options | Provider match can focus on specialty, style, and cultural needs based on profiles | Often includes multilingual support in English, Spanish, and Mandarin Chinese, depending on provider |
| Insurance and switching | May be in-network with major insurers like BCBS, Aetna, Cigna, United Healthcare, and Medicare (varies by provider/location) | Similar in-network possibilities, plus easier provider switching if the first match isn’t right |
Conclusion
Stress burnout doesn’t just appear suddenly. It starts with small signs like trouble sleeping, quick anger, and a racing mind. When it starts to hurt your health, job, or relationships, just trying harder might not work. That’s when getting help can really help.
The article shared a story about how therapy can help you recover, not just survive. It focuses on the real reasons behind burnout, like too much work, being too perfect, and poor boundaries. Using CBT, ACT, and mindfulness can help you spot triggers and change negative thoughts. Practicing these skills outside of sessions helps you stay strong under pressure.
The aim is not just to feel okay for a day and then crash again. People work towards feeling calm, thinking clearly, and sleeping better. They also want to handle stress better and set stronger boundaries. This is what recovery from burnout can look like in everyday life.
If you’re thinking about getting help, a therapy session could be a good next step. This is true if stress burnout is affecting your life. For those who prefer privacy and flexibility, virtual therapy in Texas is a great option. If you’re considering therapy, call 510-877-0950 or book an online session at https://bewellcounselingtx.com/book-an-appointment/.
FAQ
What is burnout, and how is it different from everyday stress?
Burnout is more than just feeling tired. It’s a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion caused by constant pressure. This pressure often comes from work, caregiving, or harsh personal expectations. Unlike everyday stress, burnout persists and can affect your mood, sleep, health, and relationships.
What are the three main dimensions of burnout?
Burnout is described in three main ways: energy depletion/exhaustion, increasing cynicism or negativity toward work, and reduced professional efficacy. Many people experience all three, even if they seem to be doing well on the outside.
How does burnout quietly show up in daily life?
Burnout often starts quietly. It can show up in mornings as waking up tired, in evenings as a mind that won’t switch off, and in relationships as less patience and clarity. Over time, it can feel like you’re running on empty, even when you’re doing “everything right.”
Why doesn’t burnout always improve after taking a break or a vacation?
A break can help, but burnout often doesn’t fully resolve because it’s fueled by deeper patterns and sustained overload. If the nervous system stays stuck in high alert and the same triggers are waiting when you return, symptoms often rebound quickly. Burnout recovery usually requires more than rest—it often requires structured change.
Why can modern stress feel more intense and nonstop than it used to?
Many people face higher work expectations, constant social comparison, and digital overload that leaves little quiet space. With messages, metrics, and notifications always within reach, the brain can start treating life like a constant threat. That keeps the body’s stress response “switched on” for days at a time.
What emotional burnout symptoms commonly bring people to therapy?
In emotional burnout, clients often describe numbness, irritability, mood swings, and feeling detached from what used to matter. Some feel overwhelmed, snap at loved ones, or notice a persistent sense of “I don’t care like I used to.” These are common signals of emotional burnout and chronic overload.
What cognitive signs suggest stress has progressed into burnout?
Burnout often affects thinking. Common signs include difficulty concentrating, racing thoughts, constant worry, rumination about work, decision fatigue, and “foggy” thinking. Many people are surprised to feel mentally drained even after a full night of sleep.
What physical symptoms are linked to chronic stress and burnout?
Many people report headaches, stomach issues, body tension, rapid heartbeat, chronic fatigue, and ongoing sleep problems. Frequent illness can also show up when the body stays in prolonged stress. These symptoms can feel confusing because they may not match a single medical cause, yet they track closely with work stress and emotional burnout.
What work and relationship red flags signal burnout?
Red flags often include reduced motivation, slipping performance, withdrawal from social activities, neglecting self-care, and a quiet fear of not keeping up. At home, burnout can show up as less patience, more conflict, and less emotional presence. Many people seek help when stress starts affecting work output, relationships, or health.
How does therapy explain the “stuck in high alert” feeling?
In therapy, burnout is often framed through the stress-response system. The brain can respond to a constant stream of pressures like it would to a real threat. Without intervention, the stress response may stay activated, shaping thoughts, sleep, mood, and physical health over time.
Who is most vulnerable to burnout in high-pressure roles?
Burnout can affect anyone, but it often appears in people who carry sustained responsibility and high stakes. In clinical settings, common profiles include healthcare workers, first responders, teachers, and corporate professionals. Many start out engaged and capable, then slowly feel detached, cynical, or dread returning to work.
What does a realistic burnout case profile look like in therapy?
A common case involves a high-performing professional in a demanding role who feels persistent overwhelm and runs on empty. They may report energy depletion even after sleep, growing cynicism toward work, emotional detachment, and reduced professional efficacy. They often say, “I’m still functioning, but something is off—and it’s not getting better.”
What root patterns often surface during work stress therapy?
Therapy often uncovers repeatable patterns: perfectionistic tendencies that fuel self-criticism, overextending through long hours, difficulty saying “no,” and gaps in boundary-setting and assertiveness. Unprocessed emotions can build under pressure too, including frustration, anger, grief, and in high-stress roles, guilt or helplessness after difficult events.
What skills are commonly used in burnout therapy to change the pattern?
Effective work stress therapy goes beyond quick coping tricks. Sessions often include grounding practices and guided routines to interrupt spirals, cognitive reframing (cognitive restructuring) to challenge exaggerations, emotional regulation strategies, mindfulness practices, structured problem-solving, and boundary-setting with assertiveness training. These tools are practiced until they feel usable in real life.
How do you measure progress in burnout recovery?
Progress often looks like quicker recovery after stressful moments, a calmer baseline mood, clearer thinking, better sleep patterns, and more stable emotions. Many people also notice fewer physical stress signals, less reactivity, and an increased ability to respond thoughtfully rather than react on autopilot. Stronger boundaries are another key marker.
What does burnout recovery in therapy actually look like week to week?
Burnout recovery is structured and supportive. Early sessions often focus on mapping triggers across work dynamics, personal expectations, caregiving responsibilities, and life circumstances. Later work targets skill-building, practice, and relapse prevention so the nervous system can move toward a more regulated baseline.
How does therapy “rewire” the stress response?
The goal is to move from fight-or-flight reactivity to a calmer baseline through repeated practice and new coping pathways. Therapy helps the mind interpret stress differently so the body can relax. A core principle in treatment is that the brain can change—it can unlearn unhealthy stress responses and build new ones with consistent practice.
Which evidence-based approaches are often used for burnout and emotional burnout?
Common evidence-based options include CBT, which targets negative thought cycles and adds practical coping skills; ACT, which builds psychological flexibility and values-based action; and mindfulness-based therapy such as Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction and Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy. Many clinicians integrate methods based on your needs and goals.
Why do between-session practices matter so much in burnout therapy?
Burnout recovery isn’t a quick fix, and insight alone often isn’t enough. Between sessions, clients may practice guided grounding, emotion tracking, cognitive reframing, body relaxation training, mindfulness routines, and structured problem-solving. Repetition helps the tools become second nature, reducing automatic reactivity over time.
How does therapy help prevent burnout from coming back?
Relapse prevention often focuses on strengthening boundaries, aligning actions with values, and building long-term resilience planning. A therapist can help spot blind spots, interrupt negative cycles, support you through setbacks, and create a sustainable plan. The goal is not just to “get through” stress, but to build protection against relapse.
How do I know it’s time to get help instead of trying self-guided stress tips?
Many people seek therapy when stress starts affecting work performance, relationships, or health—and when self-guided tactics like motivational quotes or generic breathing videos don’t shift the deeper pattern. If you feel stuck in a persistent state of overload, it’s a strong sign that structured support may help.
Is online counseling effective for burnout, and what are the benefits of virtual therapy Texas options?
Yes, online counseling can be effective for burnout when it’s consistent and skills-focused. Many people choose virtual therapy Texas options for privacy, flexibility, and less commute stress. Some clients also find it easier to open up from home, which can support steady progress.
How do in-person sessions compare with virtual therapy in Texas?
Both in-person and virtual formats can provide quality care. The biggest predictor of progress is often consistency and the strength of the therapeutic fit. If telehealth makes it easier to attend regularly, it can be a practical choice for burnout recovery.
What Texas access options are commonly available for therapy?
Therapy access may include support across Texas, including areas such as Sugar Land and San Antonio, with culturally sensitive care offered both virtually and in person. Many practices also offer multilingual therapy in English, Spanish, and Mandarin Chinese, plus morning, evening, and weekend availability.
What should I look for to find the right therapist for work stress therapy?
Look for deep listening, a collaborative style, and the sense that you’re understood rather than judged. Many people benefit from therapy that offers practical tools, not only conversation. Useful signs include more clarity after sessions and noticeable small improvements within a few weeks.
Can I change therapists if the fit doesn’t feel right?
Yes. Many practices allow you to choose a provider by profile and switch if the fit isn’t right. Fit matters in burnout recovery because trust and collaboration make skill-building and behavior change much easier.
Is insurance sometimes accepted for therapy, and which plans are commonly included?
Coverage varies by provider and location, but some practices are in-network with major insurers such as BCBS, Aetna, Cigna, United Healthcare, and Medicare. It’s worth confirming benefits and availability when scheduling, if you want ongoing support for burnout recovery.
Thinking about therapy—what’s the next step?
If these symptoms feel familiar, structured support can help you reset your nervous system, rebuild resilience, and recover from emotional burnout in a lasting way. Thinking about therapy? Call 510-877-0950 or schedule an online appointment when you’re ready: https://bewellcounselingtx.com/book-an-appointment/.